Prostate health is pivotal for men’s health and wellbeing but throughout their life, men can potentially face problems with their prostate. In this health guide, we’ve partnered with MoliCare® to learn more about what can trigger prostate related bladder weakness.
Is there a link between prostate health and bladder weakness?
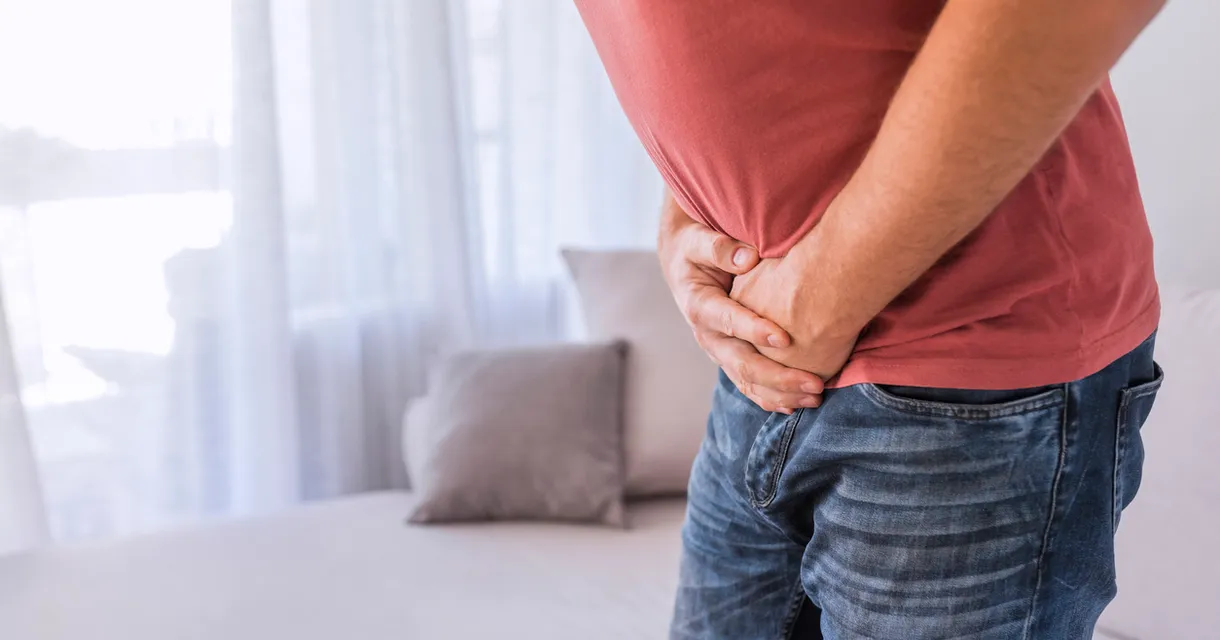
Prostate problems in men can strongly impact bladder function, leading to what is commonly known as prostate incontinence.
The prostate, a walnut-sized gland that grows larger with age, plays a key role in both reproductive and urinary health. It encircles the urethra, the tube through which urine exits the body. When the prostate is healthy, it supports normal urine flow. However, issues such as enlargement or inflammation can press against the urethra, disrupting the natural process of urination.
An enlarged prostate can also obstruct the urethra, leading to difficulties such as chronic urinary retention and other urinary issues. This condition not only causes frequent urination but can also result in a weak urine stream and a feeling that the bladder isn’t completely empty.
In severe cases, such as after prostate surgery or radiation therapy, the changes can be more drastic. Treatments might damage the nerves essential for bladder control or alter the bladder’s capacity, leading to incontinence.
Symptoms to watch out for
MoliCare® explain that it’s important for men to recognise changes that may signal prostate issues. These symptoms usually include:
- Increased frequency of urination, particularly at night.
- Difficulty initiating urination or a prolonged urinating time.
- A sensation that the bladder isn’t fully emptied after urination.
- Unexpected urges to urinate, which may lead to urine leaks.
Less common but notable symptoms include:
- Pain during urination or ejaculation.
- Presence of blood in urine or semen, which could indicate other health issues and should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider.
Common prostate problems in men
Since the prostate gland plays an important role in the urinary and reproductive functions in men, it’s easy to become disrupted. Let’s explore the most common prostate issues faced by men:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Known commonly as an enlarged prostate, BPH affects the size of the prostate gland, causing it to grow larger with age. This enlargement can impinge on the urethra, complicating normal urination. Symptoms might include increased frequency of urination, a sudden urge to urinate, and a weak urinary stream. While BPH is more common as men age, it does not escalate to prostate cancer but does require management to lessen the symptoms.
- Prostate cancer: This is the most frequent cancer among men, excluding skin cancer. The risk of developing prostate cancer escalates with age, particularly in men over 65. Family history and ethnicity can further increase the risk, with African-American men facing higher rates of incidence and more aggressive forms of the disease. Early detection through screening can be life-saving, especially for those with a family history of the condition.
- Prostatitis: Unlike other prostate conditions that typically affect older men, prostatitis can occur in both young and middle-aged individuals. It involves inflammation of the prostate, which can be acute or chronic, and is often caused by bacterial infections. Symptoms include pain, difficulty urinating, and pelvic discomfort. Chronic cases may require ongoing management, while acute infections are usually treated with antibiotics.
- Nerve problems: Around the prostate are nerves that help control how you empty the bladder. Anything damaging these nerves, like surgery or nerve diseases, can interfere with your bladder control, potentially causing pain when urinating or ejaculating. This can lead to different types of urine leaks: urge leaks (sudden urge to urinate), stress leaks (when pressure on your bladder makes urine escape), or overflow leaks (when the bladder doesn't empty completely).
- Muscle weakness: Prostate issues and treatments can weaken the muscles that control when you urinate. The prostate and its nearby muscles help seal the bladder to stop urine from leaking. But if these muscles get weak because of prostate problems, it's hard to keep urine in, and leaks can happen. Other relevant muscles in the surrounding area such as the pelvic floor muscles can be strengthened by performing kegel exercises.
Our MoliCare® recommendations for men with bladder leaks
Post-urination dribbling can be described medically as post-micturition dribble (PMD) and it can be embarrassing and frustrating for men. It ranges from a few drops after urinating, shaking after urinating but still getting a wet patch or dribbling in underwear.
- Dribble Underwear - we recommend MoliCare® Men Absorbent Underwear which are cotton briefs but with a leak proof protection zone and a slim removable pad if needed.
- Male Guards and Sheilds – we recommend MoliCare® Men Pads which are slim, discreet pads, shaped to encapsulate the genitalia so urine can’t leak onto clothing.
- Male Incontinence Underwear – we recommend MoliCare® Men Pants which are designed to look and feel like regular underwear but with a much higher absorbency can be worn for longer periods and absorb more urine.
References:
NHS. (2009) Benign prostate enlargement. [online] Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostate-enlargement/ [accessed 12/09/24]
Prostate cancer UK. (2001) Homepage. [online] Available at: https://prostatecanceruk.org/ [accessed 12/09/24]